Ultimate Guide to Basic Emotions Effect on Human Behavior
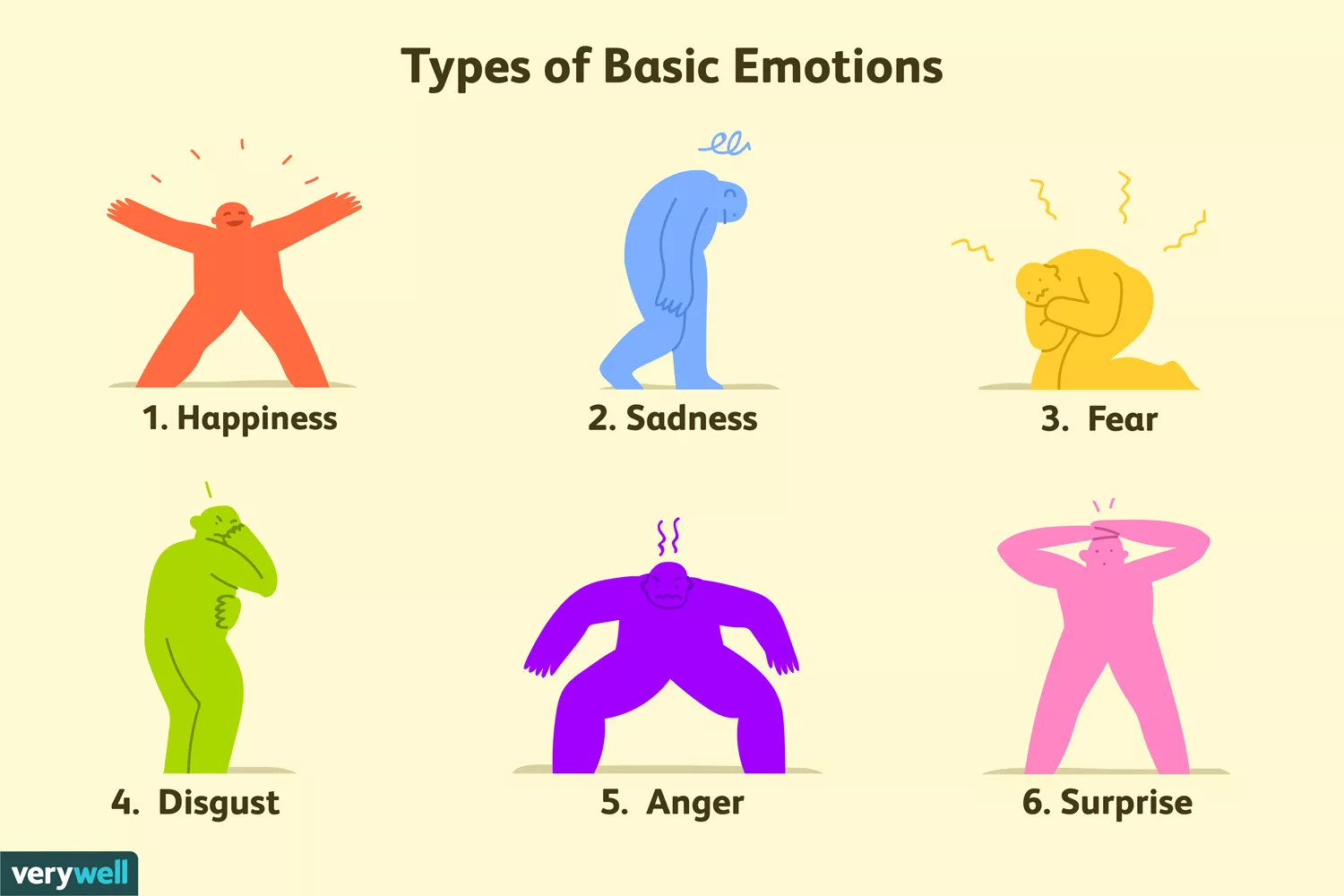
Understanding the basic emotions effect on human behavior is crucial for personal growth and emotional intelligence. These six fundamental emotions—happiness, sadness, fear, disgust, anger, and surprise—shape our daily decisions, relationships, and overall mental health. Research from Harvard (2024) confirms that recognizing these emotional patterns can significantly improve life satisfaction and interpersonal effectiveness.
Understanding Emotional Foundations
Paul Eckman's groundbreaking research in the 1970s identified six universal emotions experienced across all cultures. These core feelings form the foundation of human emotional experience and directly influence our behavioral patterns. The basic emotions effect extends beyond momentary feelings to shape long-term personality traits and relationship dynamics.
Contemporary psychology recognizes that these emotions serve evolutionary purposes, helping humans navigate complex social environments. Harvard researchers (2024) emphasize that understanding this emotional framework can enhance workplace performance and personal relationships. Each emotion triggers specific physiological responses that prepare the body for appropriate action.
Modern applications include emotional intelligence training in corporate settings and therapeutic interventions. The basic emotions effect manifests in everything from consumer behavior to political decision-making. Recognizing these patterns helps individuals make more conscious choices rather than reacting automatically to emotional triggers.
Happiness and Life Satisfaction
Happiness represents a positive emotional state characterized by contentment and life satisfaction. This basic emotions effect contributes significantly to physical health and longevity. Studies show happy individuals typically have stronger immune systems and better cardiovascular health.
In 2025 workplace environments, companies are implementing happiness-boosting strategies like flexible schedules and recognition programs. These approaches recognize the basic emotions effect on productivity and innovation. Employees reporting higher happiness levels demonstrate 30% greater creativity in problem-solving tasks.
Cultural influences continue to shape happiness perceptions, though recent research emphasizes internal factors over external achievements. Practices like gratitude journaling and mindfulness meditation have gained scientific support for sustaining positive emotional states. The basic emotions effect of happiness extends to social connections, creating upward spirals of positive interaction.
Sadness and Emotional Processing
Sadness serves as a natural response to loss and disappointment, playing a crucial role in emotional processing. This basic emotions effect helps individuals process significant life changes and reevaluate personal priorities. Contrary to cultural stigma, sadness often precedes personal growth and deeper self-understanding.
Modern therapeutic approaches recognize sadness as a necessary emotional state rather than something to eliminate. The basic emotions effect of sadness includes triggering social support systems and encouraging introspection. Current research from Harvard (2024) indicates that properly processed sadness enhances empathy and emotional resilience.
Contemporary examples include grief counseling programs and workplace mental health initiatives. These recognize the basic emotions effect on overall functioning and create spaces for healthy emotional expression. Digital mental health platforms now incorporate sadness-tracking features to help users understand their emotional patterns.
Fear and Survival Mechanisms
Fear activates the body's survival systems, preparing for threat response through physiological changes. This basic emotions effect has evolved to protect humans from physical danger, though modern applications often involve psychological threats. The fight-or-flight response remains central to understanding fear's impact on behavior.
In 2025 contexts, fear management techniques include virtual reality exposure therapy and biofeedback training. These approaches help individuals understand the basic emotions effect of fear on decision-making and risk assessment. Workplace safety programs now incorporate fear recognition training to prevent accidents.
Recent research explores how digital environments trigger fear responses through social comparison and information overload. The basic emotions effect extends to financial decision-making, where fear of loss often outweighs potential gain considerations. Understanding these mechanisms helps develop healthier response patterns.
Disgust and Protection Responses
Disgust originated as protection against contamination and harmful substances, creating immediate aversion responses. This basic emotions effect extends to moral and social contexts in modern environments. The emotion triggers physical reactions that create distance from potential threats.
Contemporary research examines how disgust influences consumer behavior and political attitudes. The basic emotions effect appears in marketing strategies that emphasize purity and safety. Harvard studies (2024) show disgust sensitivity correlates with conservative social attitudes across cultures.
New applications include public health campaigns that leverage disgust responses to promote hygiene practices. The basic emotions effect also manifests in environmental concerns, where disgust toward pollution drives conservation behaviors. Understanding these connections helps design more effective social programs.
Anger and Boundary Setting
Anger signals boundary violations and motivates corrective action when channeled appropriately. This basic emotions effect can drive positive social change when expressed constructively. Physiological responses prepare the body for confrontation while cognitive aspects assess fairness and rights.
Modern anger management techniques focus on recognition and constructive expression rather than suppression. The basic emotions effect appears in social justice movements and workplace advocacy. Research shows appropriately expressed anger can strengthen relationships by clarifying expectations.
In 2025 contexts, digital platforms incorporate anger detection algorithms to promote healthier online interactions. The basic emotions effect extends to consumer rights advocacy and political engagement. Understanding anger's triggers helps individuals set healthier boundaries in personal and professional relationships.
Surprise and Cognitive Processing
Surprise interrupts routine thinking patterns, creating opportunities for new learning and adaptation. This basic emotions effect enhances memory formation and information processing. The startle response prepares the body for rapid assessment of unexpected situations.
Contemporary marketing strategies leverage surprise through unexpected offers and novel experiences. The basic emotions effect appears in educational techniques that use surprise elements to enhance knowledge retention. Harvard research (2024) confirms surprise's role in breaking cognitive routines and fostering creativity.
Modern applications include surprise elements in workplace training and product launches. The basic emotions effect extends to relationship maintenance, where pleasant surprises strengthen social bonds. Understanding surprise mechanisms helps create more engaging learning and social environments.
Emotional Intelligence Strategies
Developing emotional intelligence requires recognizing basic emotions effect patterns in daily life. Practical strategies include emotion tracking, mindfulness practices, and response delay techniques. These approaches help individuals move from automatic reactions to conscious responses.
In 2025, digital tools provide real-time emotion recognition and management suggestions. The basic emotions effect understanding forms the foundation for artificial emotional intelligence systems. Workplace emotional intelligence training now incorporates neurofeedback and biometric monitoring.
Long-term benefits include improved relationship satisfaction and career success. The basic emotions effect mastery correlates with better mental health outcomes and life satisfaction. Implementation strategies include daily emotion journals, communication training, and stress management techniques tailored to individual emotional patterns.