Low self-esteem, a pervasive challenge in 2025, manifests as a struggle to recognize one’s inherent worth, often leading to profound self-doubt and a pervasive lack of confidence. It’s more than just an occasional bad day; it’s a deep-seated belief that one is inadequate or undeserving, impacting everything from personal relationships to professional aspirations. Recognizing the signs low self-esteem is the first critical step toward fostering a healthier self-perception. Common indicators include negative self-talk, difficulty accepting compliments, and a tendency to prioritize others’ needs over your own. Understanding these symptoms can empower individuals to seek pathways for growth and cultivate a stronger sense of self-worth.
The Challenge of Identifying Low Self-Esteem
While not officially classified as a mental illness, poor self-esteem profoundly influences an individual’s thoughts, emotions, and behavioral patterns. Its manifestations can range from overtly negative self-talk to subtle, ingrained habits like excessive people-pleasing. Sometimes, the signs low self-esteem are stark and undeniable, while at other times, they are much more nuanced, hiding beneath layers of compensatory behaviors. Regardless of its presentation, a diminished sense of personal worth and value inevitably casts a long shadow over one’s life and overall well-being. Identifying these often subtle or disguised symptoms of low self-esteem is crucial for intervention and improvement.
1. How to Recognize Low Self-Esteem in 2025
Recognizing the signs low self-esteem is the initial step towards addressing it. These indicators can manifest in various ways, from overt self-criticism to subtle patterns of behavior that undermine one’s potential. In a world increasingly shaped by digital interactions and constant comparison, understanding these signs is more relevant than ever. Being aware of these common symptoms allows for a proactive approach to mental well-being and personal development.
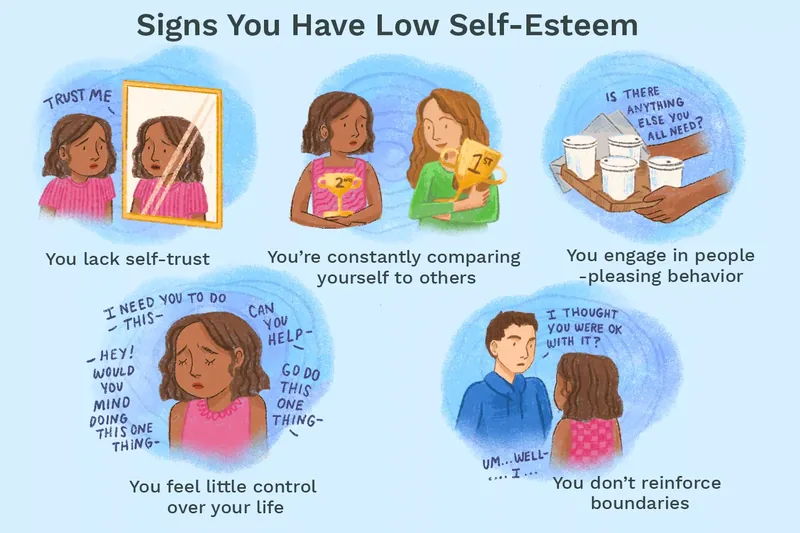
Here are the 11 common signs low self-esteem:
1. Pervasive Lack of Confidence
A fundamental sign low self-esteem is a deep-seated lack of confidence in one’s own abilities and judgment. This isn’t just about feeling nervous occasionally; it’s a consistent doubt in your capacity to handle situations, make good decisions, or succeed in endeavors. This self-distrust can prevent you from pursuing new opportunities or taking necessary risks, hindering personal and professional growth. For instance, you might consistently turn down leadership roles, not due to lack of skill, but from an inherent belief that you’re not capable of leading effectively (Harvard, 2024).
2. External Locus of Control
Individuals with low self-esteem often perceive that external forces, rather than their own actions, dictate their life’s trajectory. They believe they have minimal power to influence outcomes or initiate positive change, fostering a sense of helplessness. This belief can lead to passivity, as they feel powerless to address their problems or shape their future. This perspective can make it incredibly difficult to take personal responsibility or feel empowered to make necessary life changes.
3. Negative Social Comparisons
While social comparison can sometimes inspire, for those with low self-esteem, it often leads to detrimental self-assessment. They tend to engage in upward social comparison, consistently measuring themselves against individuals they perceive as superior in various aspects. This often leaves them feeling inadequate, hopeless, and further diminishes their self-worth. The pervasive nature of social media in 2025 can significantly exacerbate these feelings, as curated online lives present an unrealistic standard.
4. Difficulty Asking for Help
A significant indicator of low self-worth is an intense reluctance to ask for assistance or articulate personal needs. This struggle often stems from embarrassment, a fear of appearing incompetent, or a belief that one doesn’t deserve support. Such individuals may prioritize others’ desires over their own, finding it challenging to assert themselves even when genuinely in need. They might silently struggle with tasks that could easily be resolved with a little outside input, reinforcing feelings of isolation.
5. Persistent Worry and Self-Doubt
Even after making a decision, individuals with low self-esteem are plagued by persistent worry and second-guessing, constantly doubting their choices. They often defer to the opinions of others, struggling to trust their own judgment and convictions. This constant internal conflict makes decision-making arduous and can lead to significant emotional distress. This perpetual state of uncertainty can paralyze progress and prevent individuals from fully committing to their paths.
6. Trouble Accepting Compliments
One of the more subtle signs low self-esteem is an inability to genuinely accept positive feedback or compliments. Such praise often clashes with their deeply ingrained negative self-beliefs, leading to suspicion or discomfort. They might dismiss compliments, attribute success to luck, or even perceive the giver as insincere or mocking. This resistance prevents them from internalizing positive affirmations, perpetuating their cycle of self-criticism (Harvard, 2024).
7. Habitual Negative Self-Talk
A hallmark of low self-esteem is a constant internal dialogue characterized by criticism, blame, and a focus on perceived flaws. Instead of encouraging themselves, they frequently engage in negative self-talk, highlighting their shortcomings in appearance, personality, or abilities. When faced with setbacks, they are quick to internalize blame, reinforcing their negative self-perception. This relentless self-criticism erodes their confidence and well-being over time.
8. Fear of Failure
A profound fear of failure often accompanies low self-esteem, stemming from a lack of confidence in one’s capabilities. This fear can lead to either avoidance of challenges altogether or a tendency to give up quickly when difficulties arise, without genuinely exerting effort. This avoidance mechanism prevents personal growth and reinforces the belief that success is unattainable. For example, someone might avoid applying for their dream job, fearing rejection more than desiring the opportunity.
9. Poor Outlook for the Future
Individuals experiencing low self-esteem often harbor a pessimistic view of their future, feeling that positive change is unlikely or impossible. These feelings of hopelessness can severely impede their motivation to engage in behaviors that could lead to improvement or happiness. This can manifest as self-sabotaging behaviors, where they unconsciously create obstacles to prevent success, providing an external factor to blame for their lack of achievement.
10. Lack of Healthy Boundaries
A significant symptom of low self-esteem is a struggle to establish and maintain healthy personal boundaries. They may feel guilty saying no or fear alienating others, leading them to constantly accommodate requests that compromise their own needs and well-being. This lack of boundaries can result in others disrespecting their time and space, further diminishing their sense of value and increasing stress levels. It’s a clear sign low self-esteem when personal limits are constantly blurred.
11. Chronic People-Pleasing
People-pleasing is a common manifestation of low self-esteem, where individuals go to extreme lengths to ensure others’ comfort and happiness, often at their own expense. This behavior is driven by a desire for external validation, as they struggle to find self-worth internally. They frequently agree to tasks they dislike, feel immense guilt saying no, and consistently neglect their own needs in favor of others, perpetuating a cycle of self-neglect and unfulfillment.
2. The Impact of Low Self-Esteem on Your Life
Self-esteem is a foundational element for a fulfilling life, influencing your capacity to pursue goals, cultivate healthy relationships, and maintain a positive self-image. While everyone experiences occasional dips in confidence, chronic low self-esteem can significantly impair your happiness and overall life satisfaction. It not only affects your emotional state but also makes you more susceptible to a range of mental health challenges and can hinder your ability to thrive. Understanding the broad effects of low self-regard is crucial for recognizing its severity.
Research consistently highlights that lower levels of self-esteem are intricately linked to numerous mental health issues. These include, but are not limited to, generalized anxiety, eating disorders, profound emotional distress, and even problematic internet usage (Harvard, 2024). Individuals with diminished self-worth are also more prone to panic disorder, engaging in risky behaviors, and experiencing social anxiety disorder, which can severely restrict their social interactions and personal development. Furthermore, substance use and elevated stress levels are frequently observed alongside poor self-esteem, indicating a complex interplay of psychological vulnerabilities.
Beyond these direct links to mental health conditions, low self-esteem can significantly impede your life in other ways. It makes achieving personal and professional goals far more challenging, as self-doubt often leads to procrastination or outright avoidance of opportunities. Forming and maintaining healthy, supportive relationships also becomes difficult, as individuals may struggle with trust, fear rejection, or engage in unhealthy attachment patterns. Poor self-esteem can heighten sensitivity to criticism, causing individuals to internalize negative feedback more deeply than those with a stronger sense of self-worth. This increased sensitivity often leads to giving up prematurely when faced with obstacles, reinforcing the cycle of perceived failure and inadequacy. In some severe cases, low self-esteem has been identified as a risk factor for suicidal ideation, underscoring the critical importance of addressing this issue comprehensively.
3. Understanding the Root Causes of Low Self-Esteem
The development of low self-esteem is a complex interplay of various factors, often stemming from early life experiences, cognitive patterns, and environmental influences. It’s rarely a single cause but rather a combination of elements that erode an individual’s sense of worth over time. Understanding these underlying causes is essential for effective intervention and for cultivating a more robust self-perception. In the context of 2025, modern stressors and digital influences also play a notable role in shaping self-esteem.
One significant contributor is brooding, which involves being excessively preoccupied with dark or sad memories and thoughts. This constant rumination on past failures or negative experiences prevents individuals from moving forward and perpetuates a cycle of self-blame and despair. Closely related is engaging in negative self-talk or self-criticism, where an individual’s internal dialogue is consistently harsh, judgmental, and focused on perceived flaws rather than strengths. This relentless internal criticism chips away at self-worth and makes it difficult to recognize personal value.
Furthermore, the presence of a mental health disorder can significantly contribute to or exacerbate low self-esteem. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, or eating disorders often feature symptoms that directly impact self-perception, creating a feedback loop where the disorder worsens self-esteem, and poor self-esteem intensifies the disorder. Low levels of resilience, the ability to bounce back from adversity, also play a crucial role. Individuals with low resilience may find setbacks overwhelming, leading them to internalize failures and doubt their capacity to overcome future challenges. Similarly, maladaptive coping skills, like avoidance or substance use, might offer temporary relief but ultimately prevent individuals from addressing the root causes of their distress, further perpetuating feelings of inadequacy.
In the digital landscape of 2025, social media use has emerged as a significant factor. Some studies link high amounts of social media engagement, particularly in adolescents, to lower self-esteem. However, research also suggests that the purpose behind social media use is critical. If platforms are used primarily to measure popularity or likability through likes and comments, the effect can be detrimental. Conversely, using social media to connect with like-minded individuals and share interests can have a neutral or even positive impact. This nuanced understanding highlights that technology itself isn’t inherently bad, but rather how we engage with it. Finally, physical health and appearance are additional factors. For example, studies have shown that issues like untreated dental decay or missing teeth can negatively impact an individual’s self-esteem, underscoring the connection between physical well-being and psychological health (Harvard, 2024).
4. Navigating Low Self-Esteem: Coping Strategies for Today
Coping with low self-esteem, especially in the fast-paced environment of 2025, requires intentional effort and consistent practice. While building lasting self-worth is a journey, certain strategies can provide immediate relief and protect your mental well-being as you work towards deeper improvement. These approaches focus on nurturing your inner self and leveraging external support to counterbalance the pervasive effects of self-doubt. Actively engaging in these coping mechanisms can create a buffer against the negative impacts of diminished self-worth.
One powerful strategy is to focus on hopeful thoughts daily. Dedicate a small portion of your day to consciously acknowledge your strengths and achievements, no matter how minor they may seem. Allow yourself to experience genuine pride in these moments. Reflect on past challenges you’ve successfully navigated, reminding yourself of your inherent resilience and capacity to overcome difficulties. This practice helps to reframe your internal narrative, shifting focus from perceived failures to evidence of your strength and capability. It serves as a vital counterpoint to negative self-talk, helping to rewire your thought patterns over time.
Equally crucial is the practice of caring for yourself. Low self-esteem often convinces individuals that they are undeserving of kindness or consideration. It’s vital to challenge this belief by actively seeking out ways to show yourself compassion, even in small gestures. Engage in activities you genuinely enjoy, whether it’s a leisurely walk, connecting with a friend, or indulging in a beloved hobby. Prioritize rest and relaxation, recognizing that your body and mind require time to rejuvenate and regroup. Self-care isn’t a luxury or a reward you must earn; it’s an indispensable component of both physical and mental health. Investing in your own comfort and well-being sends a powerful message to yourself that you are valuable and deserving of care.
Finally, getting outside support is an invaluable coping mechanism. Sharing your struggles with a trusted individual who offers unconditional support can provide immense relief and perspective. This person could be a close friend, a family member, a mentor, a healthcare provider, or a mental health professional. Having a supportive network of people who genuinely value you and encourage you to value yourself is incredibly beneficial as you embark on the journey of improving your self-esteem. Their positive regard can serve as a mirror, reflecting your worth back to you, especially when your internal mirror is clouded by self-doubt. This external validation, when healthy, can provide the strength needed to continue the work of self-improvement (Harvard, 2024).
5. Steps to Cultivate Stronger Self-Esteem
Cultivating stronger self-esteem is an active, ongoing process that requires conscious effort and a commitment to changing ingrained thought patterns. It involves challenging deeply held beliefs about yourself and replacing them with more compassionate and realistic perspectives. These steps are designed to empower you to build a robust sense of self-worth from the inside out, fostering resilience and a healthier relationship with yourself. Engaging with these practices consistently can lead to profound and lasting positive change.
One foundational step is to notice your thoughts. Begin by becoming an observer of your daily internal dialogue, specifically identifying automatic negative thoughts. When these self-critical thoughts emerge, actively work to pinpoint cognitive distortions, such as “all-or-nothing” thinking or “jumping to conclusions.” Once identified, consciously challenge these distortions and replace them with more balanced, positive, and realistic thoughts. This practice of cognitive restructuring helps to dismantle the negative thought patterns that fuel low self-esteem. It’s about retraining your brain to default to more constructive interpretations of yourself and your experiences.
Next, learn to forgive yourself. If you tend to ruminate endlessly over past mistakes, perceived failures, or regrettable actions, it’s crucial to cultivate self-forgiveness. This doesn’t mean condoning harmful behavior, but rather releasing yourself from the burden of perpetual guilt and self-blame. By forgiving yourself, you can shift your focus from past negativity to what you can learn and do better in the future. This forward-looking perspective prevents past errors from defining your present worth and enables personal growth. It’s a powerful act of self-compassion that breaks the cycle of self-punishment.
Practice self-acceptance as a core principle. Release the notion that you must achieve perfection to be worthy of love and esteem. Instead, work on accepting yourself exactly as you are today, flaws and all. Self-acceptance acknowledges your current state without judgment, while still allowing for the desire for personal improvement. It recognizes that your inherent value is not contingent on flawless performance or external achievements. This radical self-acceptance is a powerful antidote to the constant striving and self-criticism often associated with low self-esteem, providing a stable foundation for growth.
Finally, consciously value yourself. Dedicate time to reflect on your accomplishments, talents, and unique qualities. Allow yourself to genuinely appreciate your worth without falling into the trap of social comparison or fixating on areas you wish to improve. Understand that your value is intrinsic; you don’t need to be “better” to deserve self-respect. In fact, learning to value yourself as you are often provides the very motivation and strength needed to work towards your goals. A helpful exercise is to treat yourself with the same kindness, patience, empathy, and understanding you would offer a cherished friend facing a similar struggle. Extend that same unconditional support inward, rather than engaging in self-reproach.
Additional Ways to Increase Low Self-Esteem in 2025:
- Engage in mood-boosting activities: Regularly do things that genuinely make you feel good about yourself and your capabilities.
- Stay physically active: Exercise is a proven mood enhancer and can significantly improve self-perception and confidence (Harvard, 2024).
- Acknowledge your strengths: Regularly reflect on what you excel at, reinforcing a positive self-image.
- Maintain a gratitude journal: Focusing on what you’re thankful for can shift your perspective from lack to abundance.
- Challenge negative thoughts actively: Don’t let self-critical thoughts go unchecked; question their validity.
- Surround yourself with positive people: Spend time with individuals who uplift you and make you feel valued.
- Volunteer or help others: Contributing to your community can provide a sense of purpose and accomplishment.
- Embrace imperfection: Remember that making mistakes is a universal part of the human experience.
- Celebrate every achievement: Acknowledge and celebrate both major milestones and small victories to reinforce your progress.
If you find yourself consistently struggling with signs low self-esteem, seeking professional help is a courageous and effective step. A healthcare provider or mental health professional can offer personalized treatment options. A therapist, for instance, can guide you in identifying and challenging the negative thought patterns that contribute to low self-esteem, providing tools and strategies to boost your confidence and foster a healthier opinion of yourself and your abilities. Raising your self-esteem takes time and consistent effort, but with dedication, you can learn to see and appreciate your true worth.
6. The Journey to Self-Worth: A Timeline for Growth
The path to building stronger self-esteem is not a sprint but a marathon, a gradual process that unfolds over time with consistent effort and self-compassion. There isn’t a fixed “timeline” for everyone, as individual experiences, underlying causes, and commitment to change vary greatly. However, understanding the typical phases and recognizing that progress is often incremental can help manage expectations and prevent discouragement. This journey is about cultivating new habits of thought and behavior, which, like any skill, requires practice and patience.
In the initial weeks, the focus often lies on awareness and foundational coping. This involves actively identifying the signs low self-esteem in your daily life, recognizing negative thought patterns, and starting to implement basic self-care strategies. You might begin a gratitude journal, practice mindful acceptance, or consciously reach out to one supportive friend. During this period, small shifts in perspective and behavior are significant victories. It’s about laying the groundwork, understanding that merely acknowledging the problem and taking initial steps is profound progress. Expect to feel some resistance, as challenging deeply ingrained beliefs can be uncomfortable.
As you move into the months of consistent practice, the focus shifts towards deeper cognitive restructuring and behavioral changes. This is where therapy often becomes highly effective, helping you systematically challenge cognitive distortions and develop healthier coping mechanisms. You’ll work on setting and maintaining boundaries, practicing self-forgiveness for past mistakes, and gradually exposing yourself to situations that build confidence. Progress might not be linear; there will be good days and challenging days. The key is persistence and recognizing that setbacks are part of the learning process, not a sign of failure. This phase is about solidifying new habits and beginning to internalize a more positive self-narrative. You might notice yourself accepting compliments more easily or feeling less anxious in social situations.
Over a longer period, typically six months to a year or more, the goal is to integrate these new ways of thinking and behaving into your core identity. Self-esteem becomes more stable, resilient, and less dependent on external validation. You’ll develop a stronger sense of self-acceptance, valuing yourself inherently rather than based on performance. The positive changes become more automatic, and the internal critic’s voice diminishes significantly. This stage is about sustained growth, where the tools and strategies learned become second nature, allowing you to navigate life’s challenges with greater confidence and self-assurance. The journey to self-worth is continuous, but with dedication, you can achieve a profound and lasting transformation in how you perceive and value yourself.
7. Frequently Asked Questions About Self-Esteem
What is low self-esteem?
Low self-esteem is a pervasive struggle to see one’s own worth, leading to significant self-doubt, a lack of confidence, and feeling undeserving or inadequate. It impacts how individuals value their needs, trust their abilities, and allow others to treat them, often stemming from ingrained negative beliefs about themselves.
How do I know if I have low self-esteem?
You might have low self-esteem if you consistently experience negative self-talk, difficulty accepting compliments, excessive people-pleasing, a strong fear of failure, or an external locus of control. These signs low self-esteem often lead to feelings of inadequacy and a poor outlook on the future.
Can low self-esteem be cured?
While not a disease to be “cured,” low self-esteem can be significantly improved and managed through consistent effort and various strategies. By challenging negative thoughts, practicing self-compassion, seeking support, and engaging in self-care, individuals can cultivate a stronger, healthier sense of self-worth over time.
What causes low self-esteem?
Low self-esteem can stem from various factors including negative self-talk, past experiences of criticism or failure, mental health conditions, low resilience, and even social media comparison. Early life experiences and a lack of healthy boundaries can also contribute to developing poor self-regard.